Impact Of EPA Drinking Water Stage 2 Disinfectant And Disinfectant By-Product Rule
By Randy C. Turner, Technical Director, Swan Analytical USA
Why Disinfection?
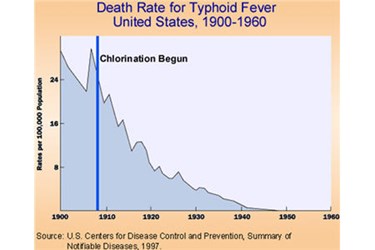
Prior to disinfection with chlorine the death rate due to typhoid fever was over 20 per 100,000 people. Disinfection with chlorine began in 1908 and deaths due to typhoid fever decreased around zero by 1960.
Chemistry of Chlorination
Free chlorine is a powerful oxidant and reacts rapidly with organic and inorganic matter. As a result, the strong disinfectant residual it initially provides may not persist as long as necessary within the distribution system. Free chlorine can readily react with organics to form unwanted disinfection byproducts (DPBs) such as trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs).
Get unlimited access to:
Enter your credentials below to log in. Not yet a member of Water Online? Subscribe today.
