Online Training: EPA's 'All-Hazards Boot Camp'

The U.S. EPA has recently released a video tutorial that outlines all phases of emergency planning and response for the water and wastewater facilities. Through a partnership of consultants, water and wastewater managers, and the EPA, this program was developed with an attention to detail. This article will introduce and give an outline to the new training from an insider’s point of view. As a disclaimer, I will state that I was one of the consultants on the panel to help create this program. However, I also endorse its usefulness, thoroughness, and overall quality to the utility as a valued resource.
The All-Hazards Boot Camp is segmented into four modules:
- Prevention and Mitigation
- Preparedness
- Response
- Recovery
EPA promotional video for the Water and Wastewater All-Hazards Boot Camp: “Don't Get Soaked: Invest in Emergency Preparedness, Prevention and Mitigation Activities”
Each of these areas is explored in real-world scenarios through the fictitious city of “Our Town” and its emergency manager. Throughout the training module there are real world pictures, charts, and video testimonials from utility professionals. Additionally, for every reference to outside materials, the EPA has provided links that open in a new web browser.
As you follow along with the presentation, there are interactive elements such as lists, figures, and pictures. This feature keeps the learner engaged in the training and not just listening passively. Each module builds on itself and gives actionable tips and suggestions throughout the training. There are quizzes along the way which must be attempted at least twice in order to continue.
Let’s review the modules.
Prevention and Mitigation
In this module the training begins with a definition of prevention, mitigation, and other key terms for emergency preparation. It outlines the concept of vulnerability and risk assessments for the utility and provides step by step guidance, with additional links, to conducting these surveys. Additionally, implementation direction is giving to the learner, with a video testimonial as a way to reinforce the importance of the plans.
Module 1 covers:
- Why and how to complete key activities associated with prevention and mitigation
- How to review and update a risk assessment (RA)
- Approaches to address vulnerabilities
- The importance of a risk management plan (RMP)
- Prevention and mitigation strategies and considerations
- How to find available resources for identifying and funding prevention/mitigation strategies
Preparedness
Module 2 teaches the student how to be ready for an emergency through a guided look at:
- How to review and update emergency response plans (ERPs)
- How to find available resources for your use
- How to identify and address gaps in resources
- How to draft and implement a training and exercise plan (TEP)
In short, the utility must be prepared for emergencies years before the event occurs in the community. Future planning, coordination, and training give the water or wastewater system team well-needed practice. This practice and training can save lives, reduce the outage time of services, and eliminate confusion from all the stakeholders of the community.
The message and the resources provided by this module alone will open the eyes of the operator or utility management to see that the federal government has the interest of the local government ever-present on their minds.
Response
In this module, the emergency event has hit the little city of “Our Town” and the planning and preparation is paying off. The subjects covered in this module are:
- How to activate and implement you ERP
- How to communicate and coordinate with response partners and the public
- The importance of activating mutual aid agreements and requesting resources
- The importance of conducting repairs and taking actions to return your utility to service
- How to maintain documentation of damages and repair work
- How to find available resources for developing your own response procedures and policies
When an emergency hits the treatment works, then the planning activities go live. Therefore, it is necessary to set up an Incident Command System (ICS) and initiate the Incident Action Plan (IAP). During this module you get a simulated scenario, which shows the immense coordination and response efforts needed to provide uninterrupted service (or briefly interrupted service) to the local community. In the video testimonial, I give a description of how my former utility recovered from a hurricane event.
Recovery
After the event, the utility leadership must look to long-term efforts to move back into the mitigation and preparedness phases.
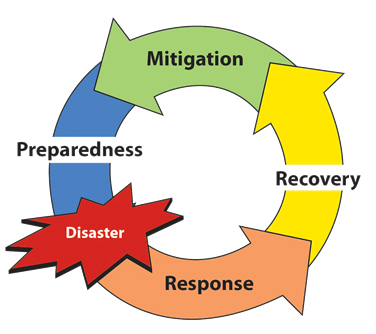
Image credit: Arete Healthcare Services
Module 4 students will learn:
- How to develop, activate, and use recovery plans
- How to communicate and coordinate with recovery partners and the public
- How to request and demobilize resources
- About conducting permanent repair work
- The importance of taking actions to return your utility to service
- How to compile documentation of damages and repair work
- How to apply for disaster-related funding and financial assistance
- The importance of conducting after-action assessments to update prevention, mitigation, and preparedness activities
- How to find resources available to implement recovery activities
In the end, the Water and Wastewater All-Hazards Boot Camp training course is a unique and thorough course for all levels of the utility. If this resource by itself isn’t a great motivator to have all employees take the course, many states have pre-approved the Boot Camp training for 0.2 CECs or 2.0 training hours. Don’t be left unprepared in case of an emergency. Let the EPA assist your utility with the 100 percent free, value-added course.
